How to pronounce papier
Do you find the information below useful? If you do, you can get guides like it for 1,000+ French words by downloading this app for your iPhone or iPad.
| l | 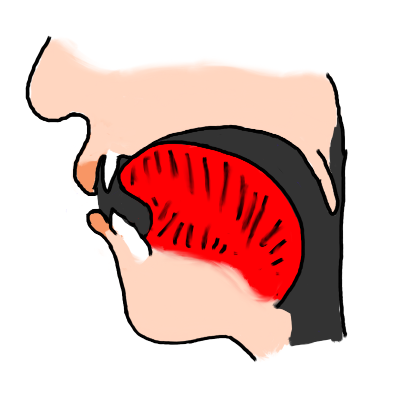 | The French 'l' is similar to the 'l' in English "with Lee". The tongue tip usually touches the back of the upper teeth. It is also a so-called "clear" l: in other words, you don't raise the back of your tongue as you pronounce the French 'l', as occurs in some cases in English. | |
| ə | 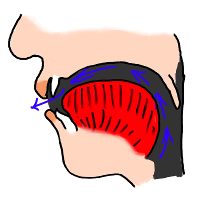 | The 'schwa' or 'neutral e' is pronounced with the tongue in a "central, relaxed" position and the mouth also in a 'half open, relaxed' position. Note that many French speakers actually tend to pronounce this vowel as a 'close eu' vowel (as occurs at the end of words ending in -euse), or at least with some rounding of the lips. | |
| p | 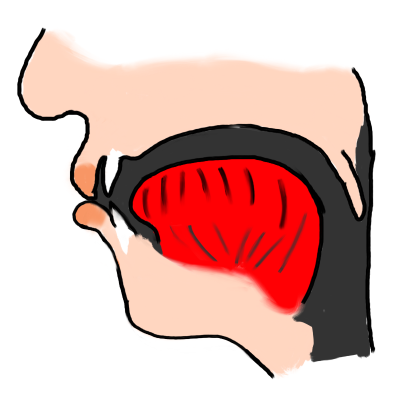 | A French 'p' is generally pronounced in a similar way to an English 'p' in "spit", "sport" etc. In other words, it is not usually followed by a "strong burst of air" (aspiration) as in the 'p' sound of English "pit", "port" etc. If you are a native English speaker, put your hand in front of your mouth while you say "port" then "sport"; you'll feel a stronger breath of air with the first of these words. When you pronounce a French 'p' sound, you do so as in the second of these words, so that you don't hear or feel the strong breath of air. | |
| a | 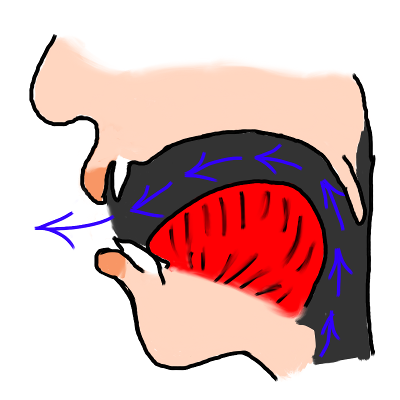 | The French 'a' vowel is pronounced with the tongue far forward in the mouth and the mouth quite wide open, but not quite as open as for a typical English 'a' vowel. | |
| p |  | A French 'p' is generally pronounced in a similar way to an English 'p' in "spit", "sport" etc. In other words, it is not usually followed by a "strong burst of air" (aspiration) as in the 'p' sound of English "pit", "port" etc. If you are a native English speaker, put your hand in front of your mouth while you say "port" then "sport"; you'll feel a stronger breath of air with the first of these words. When you pronounce a French 'p' sound, you do so as in the second of these words, so that you don't hear or feel the strong breath of air. | |
| j | 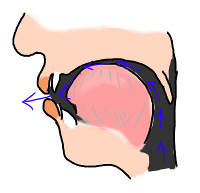 | This is a sound a little like an English "y" as in "yes". To pronounce it, you "glide" rapidly between a French 'i' vowel and the following vowel. (And on the end of a word, you pronounce it by going rapidly from the previous vowel to a French 'i' vowel.) Note the phonetic symbol [j] doesn't mean the sound at the start of "je" or "jean". | You might have expected this sound to be a normal i vowel here. However, whenever i is followed by another vowel in French, the two vowels generally "merge" together (technically speaking, they form a diphthong). In other words, you start in the position for a normal i vowel, but then "glide" into the second vowel, which is what you hear in this case. |
| e | 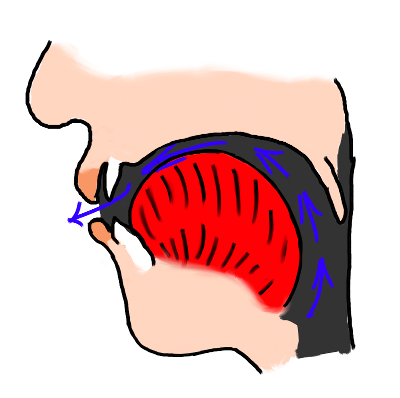 | The French 'close e' vowel, often written é, is pronounced with the tongue almost as far forward in the mouth as it will go, and fairly close to the roof of the mouth. Keep your lips fairly spread and aim to "hold your tongue and lips in position" (to avoid producing it as a "glide" or diphthong) as you pronounce it. |